Guide to Ghana
Background on Ghana
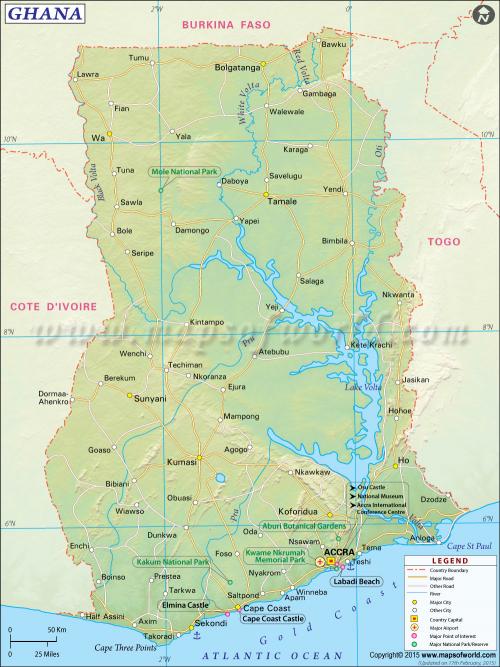
Ghana officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country located along the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean, in the sub region of West Africa. Spanning a land mass of 238,535 km2 (92,099 sq mi), Ghana is bordered by the Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, Togo in the east, and the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean in the south. Ghana means "Warrior King" in the Soninke language.
The first permanent state in the territory of present-day Ghana dates back to the 11th century. Numerous kingdoms and empires emerged over the centuries, of which the most powerful was the Kingdom of Ashanti. Beginning in the 15th century, the Portuguese Empire, followed by numerous other European powers, contested the area for trading rights, until the British ultimately established control of the coast by the late 19th century. Following over a century of native resistance, Ghana's current borders were established by the 1900s as the British Gold Coast. It became independent of the United Kingdom on 6 March 1957.
Ghana's population of approximately 30 million spans a variety of ethnic, linguistic and religious groups. According to the 2010 census, 71.2% of the population was Christian, 17.6% was Muslim, and 5.2% practiced traditional faiths Its diverse geography and ecology ranges from coastal savannahs to tropical rain forests.
Ghana is a unitary constitutional democracy led by a president who is both head of state and head of the government. Ghana's growing economic prosperity and democratic political system have made it a regional power in West Africa It is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, the African Union, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), Group of 24 (G24) and the Commonwealth of Nations.
English is the official language and lingua franca.
Additionally, there are eleven languages that have the status of government-sponsored languages:
- Ga
- four Akan languages (Asante Twi, Akuapem Twi, Fante and Nzema)
- two Mole-Dagbani ethnic languages (Dagaare and Dagbanli)
- Ewe
- Dangme
- Guan
- Kasem
Of these, Akan is the most widely spoken
Since Ghana is surrounded by French-speaking countries, French is widely taught in schools and universities, as well as a language used for commercial and international economic exchanges. Since 2006, Ghana has been an associate member of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, the global organization that unites French-speaking countries (84 nations on 6 continents). In 2005, over 350 000 Ghanaian children studied French in schools. Since then, its status has progressively been updated to a mandatory language in every high school.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghana
Cashew and the Ghanaian economy
The Tanzanian economy is heavily based on agriculture, which in 2013 accounted for 24.5 percent of gross domestic product, provides 85% of exports, and accounted for half of the employed workforce. Cashew nuts have been grown on a commercial scale in the country since the 1950s.The industry almost collapsed in the 1980s. Annual production had dropped as low as 20,000 tonnes in 1986. Economic reforms began to take place after this near collapse with the goal of reviving the troubled industry. There has been a remarkable recovery since then. In just 10 years from 1990-1999, cashew nut production went from approximately 29,000 tonnes to 120,000 tonnes. Most recently Tanzania achieves a production of about 300,000 MT. More than eighty-five percent of the farmers are small holder farmers and have an average farm size of 1 hectare. Most farmers are the elderly and rely on manual labour rather than machinery. Most youth from the rural areas prefer to move to the urban areas as cashew farming is less appealing to them. The main production is located in the southern part of the country with Mtwara contributing 70% of the national output in 2011. Over 90% of the national harvest is exported to India for processing. Recently Vietnam also began the purchase of Tanzanian cashew crops. Currently the country has 4 major cashew processors as follows. These four processors do not come close to the national output and there has been government interest to revive and open new processing plants.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cashew_production_in_Tanzania
Accra: Main Conference Location
Accra (/əˈkrɑː/;Akuapem & Asante Twi: Nkran) is the capital of Ghana covering an area of 225.67 km2 (87.13 sq mi) with an estimated urban population of 2.27 million as of 2012. It is organized into 12 local government districts – 11 municipal districts and the Accra Metropolitan District, which is the only district within the capital to be granted city status. "Accra" usually refers to the Accra Metropolitan Area, which serves as the capital of Ghana, while the district which is within the jurisdiction of the Accra Metropolitan Assembly is distinguished from the rest of the capital as the "City of Accra". In common usage, however, the terms "Accra" and "City of Accra" are used interchangeably.
The intersection of the Lafa stream and Mallam junction serves as the western border of Accra, the Great Hall of the University of Ghana forms Accra's northern border, while the Nautical College forms the eastern border. The Gulf of Guinea forms the southern border.
Formed from the merger of distinct settlements around British Fort James, Dutch Fort Crêvecoeur (Ussher Fort), and Danish Fort Christiansborg as Jamestown, Usshertown, and Christiansborg respectively, Accra served as the capital of the British Gold Coast between 1877 and 1957 and has since transitioned into a modern metropolis. The capital's architecture reflects this history, ranging from 19th-century colonial architecture to modern skyscrapers and apartment blocks.
Accra is the Greater Accra Region's economic and administrative hub, and serves as the anchor of the larger Greater Accra Metropolitan Area (GAMA), which is inhabited by about 4 million people, making it the thirteenth-largest metropolitan area in Africa. Strategic initiatives, such as transportation, are coordinated between the local government authorities, while the Accra Metropolitan Assembly, based in West Ridge, is responsible for the administration of the 60 km2 (23 sq mi) City of Accra only.
Accra is the most densely populated city in Ghana. The central business district of Accra contains the city's main banks and department stores, as well as an area known as the Ministries, where Ghana's government administration is concentrated. Economic activities in Accra include the financial and commercial sectors, fishing and the manufacture of processed food, lumber, plywood, textiles, clothing and chemicals. Tourism is becoming a thriving source of business for those in arts and crafts, historical sites and local travel and tour agents. The Oxford Street in the district of Osu has grown to become the hub of business and night life in Accra.
In 2010, the Globalization and World Cities Research Network think tank designated Accra as a Gamma level world city, indicating a growing level of international influence and connectedness
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Accra
Currency
The local currency is the Ghanaian cedi (GHS). Click here to view the exchange rate from GHS to USD.
Health
To receive accurate and up-to-date information on general health information for travelers to Ghana, please click here.
Please make sure to check if a yellow fever vaccination certificate will be required for your immigration to Ghana.
Climate
The climate of Ghana is tropical and there are two main seasons: the wet season and the dry season.